命令模式
命令模式(Command Pattern)是一种行为设计模式,它将请求封装为独立对象,允许用户参数化客户端对象,并支持请求排队、记录请求日志、撤销操作等高级功能。

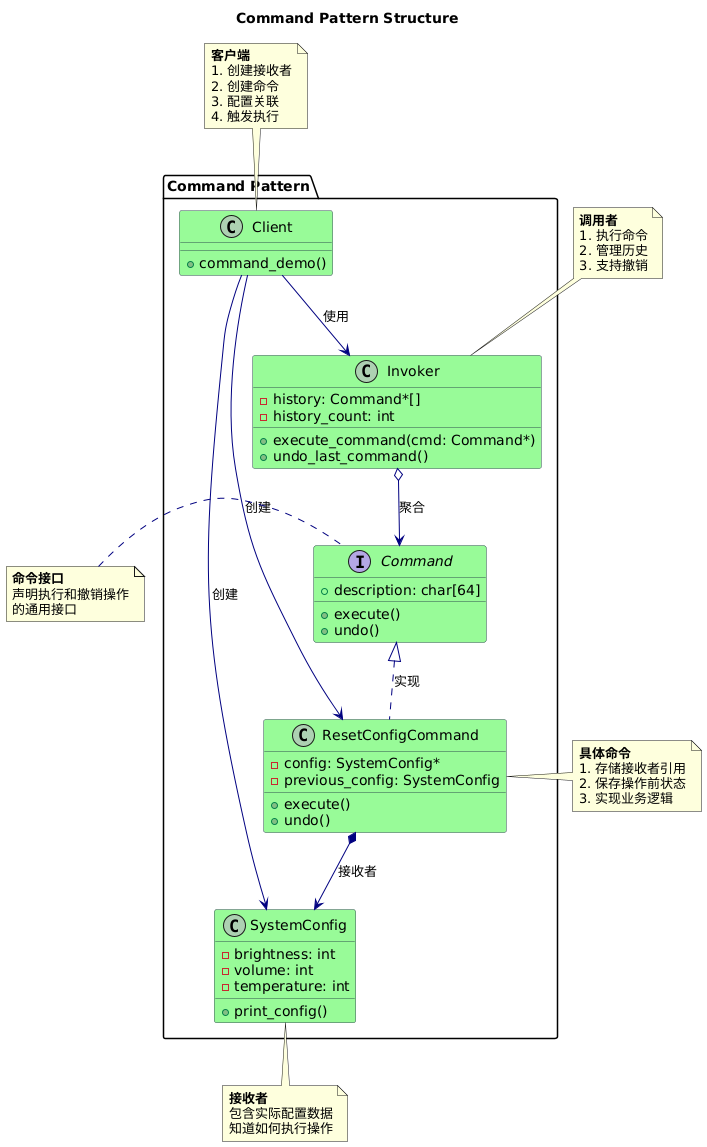
命令模式包含以下主要角色:
Invoker(调用者):要求命令对象执行请求,通常会持有命令对象,可以持有很多的命令对象。
Command(命令接口):声明执行操作的接口。
ConcreteCommand(具体命令):将一个接收者对象绑定于一个动作,调用接收者相应的操作。
Receiver(接收者):知道如何实施与执行一个请求相关的操作,任何类都可能作为一个接收者。
Client(客户端):创建具体命令对象并设定其接收者。
嵌入式应用案例
嵌入式中有些需求需要按组设置一些配置参数,如果误触发了重置配置参数的操作,还需要能撤销为上一次的设置。
例如,一个配置参数管理的场景:亮度、音量、温度这三个参数的管理。要求:能够撤销到上一个配置状态。
结构图:
1、命令接口(Command):
定义所有命令的通用接口 包含执行( execute)和撤销(undo)方法包含操作描述( description)
typedef struct Command Command;
struct Command
{
void (*execute)(Command*);
void (*undo)(Command*);
char description[64];
};
2、具体命令(ResetConfigCommand):
持有接收者( SystemConfig)的引用在执行时保存接收者状态( previous_config)实现具体的业务逻辑(重置配置)
typedef struct
{
Command base; // 继承命令接口
SystemConfig* config;
SystemConfig previous_config;
} ResetConfigCommand;
void reset_execute(Command* cmd)
{
ResetConfigCommand* rcc = (ResetConfigCommand*)cmd;
rcc->previous_config = *rcc->config; // 保存当前配置
// 重置为默认值
rcc->config->brightness = 50;
rcc->config->volume = 50;
rcc->config->temperature = 22;
strcpy(cmd->description, "Reset all parameters");
printf("Executed: %s\n", cmd->description);
}
void reset_undo(Command* cmd)
{
ResetConfigCommand* rcc = (ResetConfigCommand*)cmd;
*rcc->config = rcc->previous_config; // 恢复之前配置
printf("Reverted reset operation\n");
}
Command* create_reset_command(SystemConfig* config)
{
ResetConfigCommand* cmd = malloc(sizeof(ResetConfigCommand));
cmd->base.execute = reset_execute;
cmd->base.undo = reset_undo;
cmd->config = config;
return (Command*)cmd;
}
3、 接收者(SystemConfig):
实际存储配置数据的对象 不直接参与命令执行流程 通过命令被间接操作
typedef struct
{
int brightness;
int volume;
int temperature;
} SystemConfig;
4、调用者(Invoker):
核心调度中心 管理命令历史记录 提供执行和撤销功能 不依赖具体命令类型
Command* history[MAX_HISTORY];
int history_count = 0;
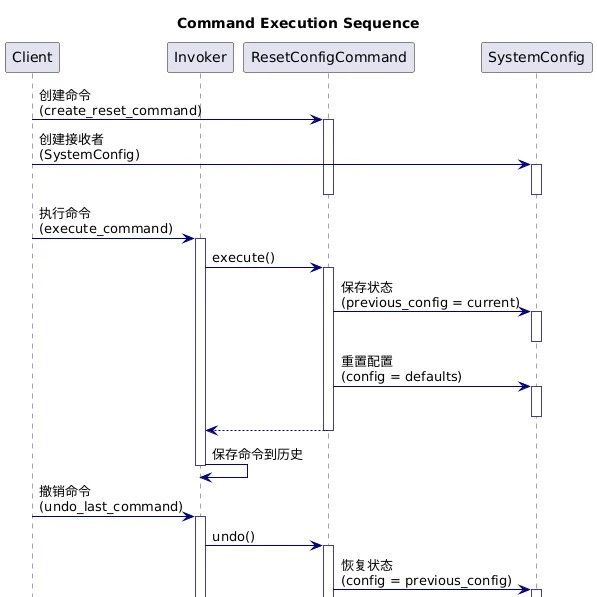
void execute_command(Command* cmd)
{
cmd->execute(cmd);
if (history_count < MAX_HISTORY)
{
history[history_count++] = cmd;
}
}
void undo_last_command(void)
{
if (history_count > 0)
{
Command* cmd = history[--history_count];
printf("Undo: %s\n", cmd->description);
cmd->undo(cmd);
}
}
5、客户端(Client):
组装命令对象 配置命令与接收者的关系 触发命令执行流程 负责资源清理
void command_demo(void)
{
// 创建接收者
SystemConfig current_config = {60, 40, 30};
// 创建具体命令
Command* reset_cmd = create_reset_command(¤t_config);
// 通过调用者执行命令
execute_command(reset_cmd);
// 通过调用者撤销命令
undo_last_command();
// 清理资源
free(reset_cmd);
}
序列图:
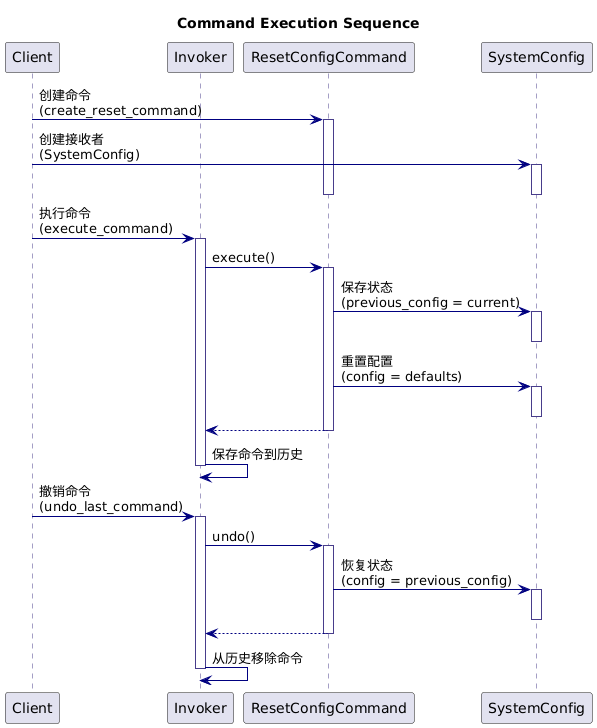
1、代码实现
C语言:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
// 配置参数结构
typedefstruct
{
int brightness; // 亮度 (0-100)
int volume; // 音量 (0-100)
int temperature; // 温度 (10-30°C)
} SystemConfig;
// 打印配置
void print_config(const SystemConfig* config, const char* title)
{
printf("%s:\n", title);
printf(" Brightness: %d%%\n", config->brightness);
printf(" Volume: %d%%\n", config->volume);
printf(" Temperature: %d°C\n\n", config->temperature);
}
// 命令接口
typedefstruct Command Command;
struct Command
{
void (*execute)(Command*);
void (*undo)(Command*);
char description[64];
};
// 命令历史记录
#define MAX_HISTORY 10
Command* history[MAX_HISTORY];
int history_count = 0;
void execute_command(Command* cmd)
{
cmd->execute(cmd);
if (history_count < MAX_HISTORY)
{
history[history_count++] = cmd;
}
}
void undo_last_command(void)
{
if (history_count > 0)
{
Command* cmd = history[--history_count];
printf("Undo: %s\n", cmd->description);
cmd->undo(cmd);
}
}
// 重置配置命令
typedefstruct
{
Command base;
SystemConfig* config;
SystemConfig previous_config; // 保存重置前的完整配置
} ResetConfigCommand;
void reset_execute(Command* cmd)
{
ResetConfigCommand* rcc = (ResetConfigCommand*)cmd;
rcc->previous_config = *rcc->config; // 保存当前配置
// 重置为默认值
rcc->config->brightness = 50;
rcc->config->volume = 50;
rcc->config->temperature = 22;
strcpy(cmd->description, "Reset all parameters");
printf("Executed: %s\n", cmd->description);
}
void reset_undo(Command* cmd)
{
ResetConfigCommand* rcc = (ResetConfigCommand*)cmd;
*rcc->config = rcc->previous_config; // 恢复之前配置
printf("Reverted reset operation\n");
}
Command* create_reset_command(SystemConfig* config)
{
ResetConfigCommand* cmd = malloc(sizeof(ResetConfigCommand));
cmd->base.execute = reset_execute;
cmd->base.undo = reset_undo;
cmd->config = config;
return (Command*)cmd;
}
void command_demo(void)
{
printf("===== Command Pattern Demo =====\n");
// 批量设置系统配置
SystemConfig current_config = {60, 40, 30};
print_config(¤t_config, "Batch Config");
// 误操作:重置配置
Command* reset_cmd = create_reset_command(¤t_config);
execute_command(reset_cmd);
print_config(¤t_config, "After Reset (Mistake)");
// 撤销重置操作
printf("--- Undo reset command ---\n");
undo_last_command();
print_config(¤t_config, "After Undo Reset");
printf("================================\n");
// 清理内存
free(reset_cmd);
}
int main(void)
{
command_demo();
return0;
}

这个例子中具体命令只有一个:重置配置命令。使用命令模式可以很方便地扩展其它命令,如:
创建一个批量设置命令:继承命令接口,并实现对应批量设置命令的逻辑。
// 批量设置命令
typedefstruct {
Command base;
SystemConfig* config;
SystemConfig new_config;
SystemConfig previous_config;
} BatchSetCommand;
void batch_set_execute(Command* cmd) {
BatchSetCommand* bsc = (BatchSetCommand*)cmd;
bsc->previous_config = *bsc->config; // 保存当前配置
*bsc->config = bsc->new_config; // 应用新配置
snprintf(cmd->description, 50, "Batch set: B=%d%%, V=%d%%, T=%d°C",
bsc->new_config.brightness,
bsc->new_config.volume,
bsc->new_config.temperature);
printf("Executed: %s\n", cmd->description);
}
void batch_set_undo(Command* cmd) {
BatchSetCommand* bsc = (BatchSetCommand*)cmd;
*bsc->config = bsc->previous_config; // 恢复之前配置
printf("Reverted batch settings\n");
}
Command* create_batch_set_command(SystemConfig* config,
int brightness, int volume, int temp) {
BatchSetCommand* cmd = malloc(sizeof(BatchSetCommand));
cmd->base.execute = batch_set_execute;
cmd->base.undo = batch_set_undo;
cmd->config = config;
// 设置新配置值
cmd->new_config.brightness = brightness;
cmd->new_config.volume = volume;
cmd->new_config.temperature = temp;
return (Command*)cmd;
}
C++:
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <string>
#include <memory>
// 配置参数结构
class SystemConfig {
public:
int brightness; // 亮度 (0-100)
int volume; // 音量 (0-100)
int temperature; // 温度 (10-30°C)
SystemConfig(int b = 50, int v = 50, int t = 22)
: brightness(b), volume(v), temperature(t) {}
void print(const std::string& title) const {
std::cout << title << ":\n";
std::cout << " Brightness: " << brightness << "%\n";
std::cout << " Volume: " << volume << "%\n";
std::cout << " Temperature: " << temperature << "°C\n\n";
}
};
// 命令接口
class Command {
public:
virtual ~Command() = default;
virtual void execute() = 0;
virtual void undo() = 0;
virtual std::string getDescription() const = 0;
};
// 调用者 (Invoker)
class CommandInvoker {
private:
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<Command>> history;
staticconstsize_t MAX_HISTORY = 10;
public:
void executeCommand(std::unique_ptr<Command> cmd) {
cmd->execute();
if (history.size() < MAX_HISTORY) {
history.push_back(std::move(cmd));
}
}
void undoLastCommand() {
if (!history.empty()) {
std::cout << "Undo: " << history.back()->getDescription() << "\n";
history.back()->undo();
history.pop_back();
}
}
};
// 具体命令:重置配置命令
class ResetConfigCommand :public Command {
private:
SystemConfig& config;
SystemConfig previousConfig;
std::string description = "Reset all parameters";
public:
ResetConfigCommand(SystemConfig& cfg) : config(cfg) {}
void execute() override {
previousConfig = config;
config = SystemConfig(50, 50, 22);
std::cout << "Executed: " << description << "\n";
}
void undo() override {
config = previousConfig;
std::cout << "Reverted reset operation\n";
}
std::string getDescription() const override {
return description;
}
};
// 客户端
void commandDemo() {
std::cout << "===== Command Pattern Demo =====\n";
// 批量设置系统配置
SystemConfig currentConfig(60, 40, 30);
currentConfig.print("Batch Config");
// 创建调用者
CommandInvoker invoker;
// 误操作:重置配置
invoker.executeCommand(std::make_unique<ResetConfigCommand>(currentConfig));
currentConfig.print("After Reset (Mistake)");
// 撤销重置操作
std::cout << "--- Undo reset command ---\n";
invoker.undoLastCommand();
currentConfig.print("After Undo Reset");
std::cout << "======================================\n";
}
int main() {
commandDemo();
return0;
}
2、命令模式优缺点
优点:
解耦:分离请求发起者和执行者 可扩展:新增命令无需修改现有代码 支持高级操作:内置撤销/重做功能
缺点:
类膨胀:每个命令需单独类 间接调用:增加系统复杂度
嵌入式场景适用性总结
在需要操作队列、撤销功能或硬件抽象层的嵌入式系统中可以考虑使用命令模式,简单操作可直接调用避免过度设计。