
点击蓝字 关注我们

欢迎各位专家学者在公众号平台报道最新研究工作,荐稿请联系小编Robert(微信ID:BrainX007); 或将稿件发送至lgl010@vip.163.com。
英文标题:Ultra‑sensitive electrochemical sensor based on molecularly imprinted polydopamine grafted with MWCNT‑COOH for tryptophan detection

成果简介
色氨酸(Trp)是一种人体必需氨基酸,在蛋白质合成、神经递质(如血清素和褪黑激素)生成及代谢调节中发挥关键作用。其血浆浓度正常范围为40–100 μM,水平异常会与代谢综合征、肝脏疾病及遗传性紊乱密切相关。目前,液相色谱-质谱(LC-MS)、高效液相色谱(HPLC)和荧光光谱等传统检测方法虽可实现定量分析,但存在设备昂贵、前处理复杂、抗干扰能力弱等局限性。电化学传感器凭借高灵敏度、低成本、操作简便等优势,成为精准检测Trp的理想替代方案。
为此,伊朗Azarbaijan Shahid Madani大学Habib Razmi团队开发了一种基于羧基化多壁碳纳米管(MWCNT-COOH)与分子印迹聚多巴胺(PDA-MIP)复合结构的超灵敏色氨酸电化学传感器。该传感器通过多巴胺在MWCNT-COOH和Trp存在下的自聚合反应形成印迹空腔,移除模板分子后形成高度特异性的识别位点。MWCNT-COOH不仅显著提升基底导电性和比表面积,还通过羧基官能团增强与目标分子的相互作用。在最优的实验条件下,该传感器对Trp表现出卓越的选择性和灵敏度,线性范围覆盖10⁻¹⁴ M至10⁻⁴ M,检测限低至4.33×10⁻¹⁵ M。在实际血清和牛奶样本检测中,回收率稳定在95.0%–106.6%,验证了其在复杂生物基质中的可靠应用潜力。
研究亮点
功能化纳米复合基底设计:MWCNT-COOH通过酸处理引入羧基官能团,增强分散性和界面相容性;以多巴胺为功能单体,在Trp模板存在下通过自聚合形成PDA-MIP层,结合MWCNT-COOH的羧基修饰,通过自聚合形成三维网络结构,提供高密度印迹位点,显著降低电荷转移电阻(Rct从121.77 Ω降至71.29 Ω),提升识别位点密度与电子转移效率。
超灵敏检测性能:线性范围横跨10个数量级(10⁻¹⁴–10⁻⁴ M),检测限达4.33×10⁻¹⁵ M,在结构类似物(酪氨酸、多巴胺等)及高浓度葡萄糖存在下仍保持高选择性。
优异实际应用表现:MWCNT-COOH与PDA-MIP复合电极在血清与牛奶复杂基质中抗干扰能力强,对结构类似物(酪氨酸、多巴胺等)信号波动<5%,回收率稳定在95.0%–106.6%,为疾病诊断、食品质量监控及药物分析提供了可靠工具。
图文解析

Fig. 1. Schematic representation of the developed electrochemical sensor based on molecular imprinted polydopamine grafted with MWCNT-COOH for tryptophan detection.
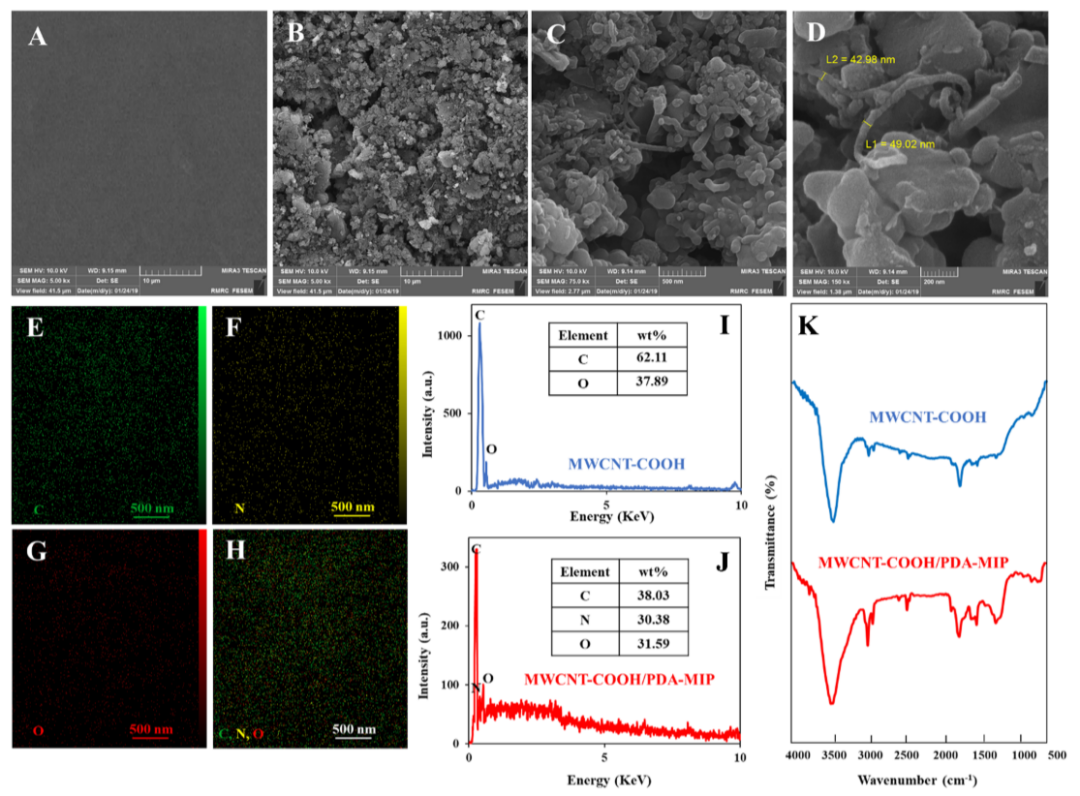
Fig. 2. FE-SEM images of A bare GCE and B-D MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP in various magnifications.E-H approves the elemental mapping analysis of MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP with a good distribution of C, O, and N. I-J EDS of MWCNT-COOH and MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP. K The FT-IR spectra of MWCNT-COOH and MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP.
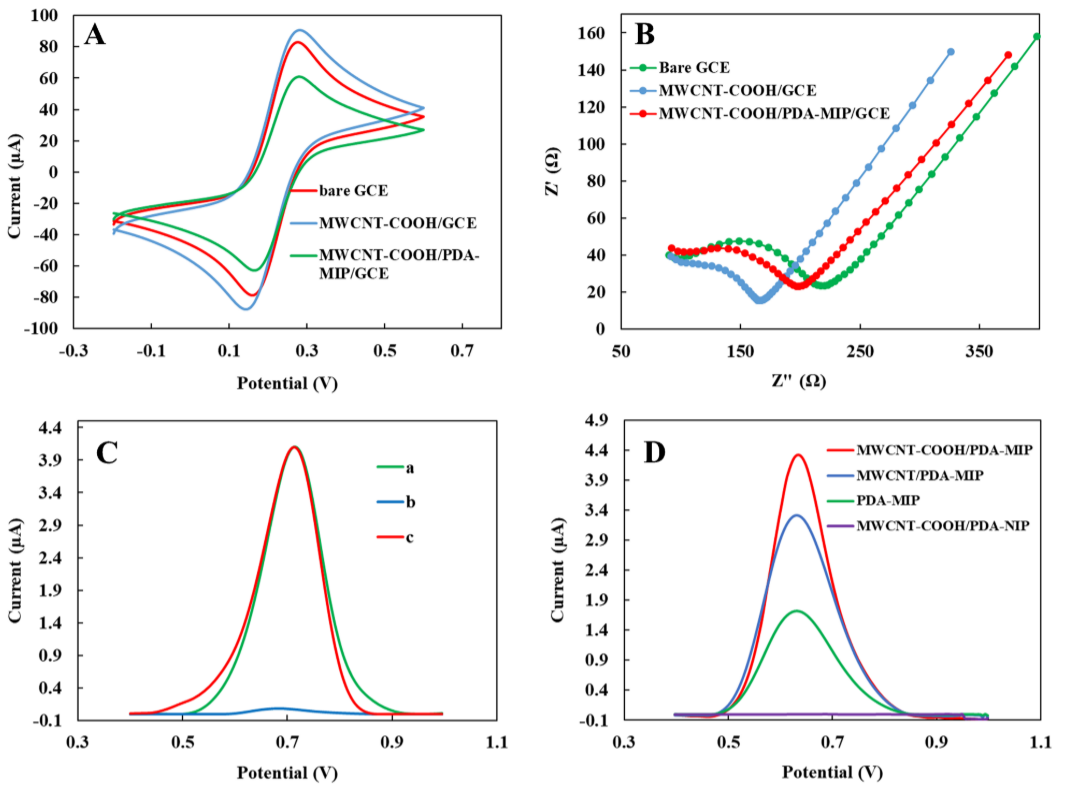
Fig. 3. Investigation of the electrochemical behavior: A. CVs and B. EIS of GCE, MWCNT-COOH/GCE, and MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP/GCE in a 10 mM [Fe(CN)6]3-/4- containing 0.1 M KCl solu-tion. C. DPVs of the MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP/GCE electrode with (a) molecular Trp template intact, (b) the electrode after templateremoval, and (c) the electrode after reloading the Trp. D. Comparative DPVs of GCE modified with MWCNT-COOH/PDA-NIP,PDA-MIP,MWCNT/PDA-MIP,and MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP in 0.1 M PBS at pH 7. Experimental conditions include a 6-min loading time in a 1 mM Trp solution and a 6-min analyte removal time using methanol and sulfuric acid solution in a 4:1 ratio.

Fig. 4. A. CVs of the MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP/GCE electrode prepared with varying volumes of the modifier dispersion (1–5 μL) in 0.1 M PBS (pH 7) at a scan rate of 50 mV/s, with 6 min of analyte loading (1 mM solution) and 6 min of removal time in a 4:1 methanol-sulfuric acid solution. B. Relationship between the polymer volume and the electrode response. C. CVs of the modified GCE in the same PBS solution at a scan rate of 50 mV/s, using a fixed 8-min analyte loading time and varying removal times in the methanol-sulfuric acid solution (4:1 ratio). D. Correlation between sensor response and analyte removal time. E. CVs of the modified electrode in phosphate buffer, with different analyte loading times (1 mM solution), and a fixed 8-min removal time. F. Correlation between sensor response and analyte loading time

Fig. 5. A. CVs of GCE modified with MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP prepared from dispersions of MIP containing different analyte-to-monomer ratios: (a)dopamine to Trp ratio of 1:2, (b)dopamine to Trp ratio of 1:1, (c)dopamine to Trp ratio of 2:1,and (d) dopamine to Trp ratio of 1.5:1 in 0.1 M phosphate buffer solution at pH 7. B. Related histogram. C. DPVs obtained from the MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP prepared at various temperatures in 0.1 M PBS (pH = 7) after Trp loading. D. Variation of Trp peak current as a function of polymer synthesis temperature. E. DPVs obtained from the modified electrode prepared at different pH values.F. Variation of Trp peak cur-rent as a function of polymer synthesis pH. G. Relationship between peak potential and pH.Other conditions: 8-min loading time in 1 μM analyte solution and 8-min removal time in a 4:1 methanol–sulfuric acid solution.

Fig. 6. A. DPVs of the designed sensor at varying [Trp] ranging from 10 −14 M to 10−9 M and B. from 10−8 M to 10−4 M in 0.1 M PBS (pH = 7). C. A linear relationship between the logarithmic concentra-tion of Trp in the range of 10−14 M to 10−9 M and peak current, and D. in the range of 10−8 M to 10−4 M.
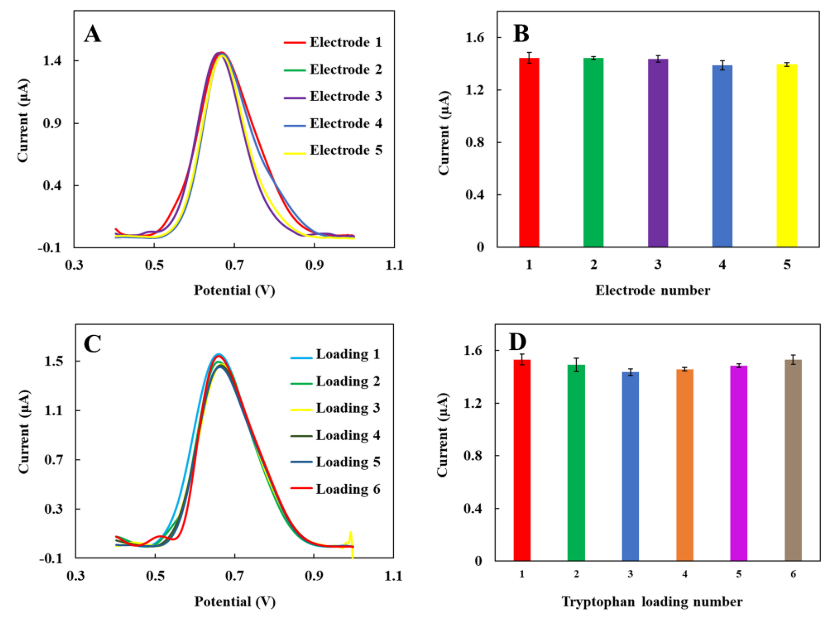
Fig. 7. A. Voltammograms demonstrating the reproducibility of the designed sensor platform prepared on five different GCEs under iden-tical conditions, measured in 0.1 M PBS at pH 7. B. Corresponding histograms illustrating response reproducibility. C. DPVs showing the stability of the sensor during six cycles of analyte removal and reloading, each with an 8-min loading period in a 1 μM analyte solu-tion followed by an 8-min removal period in a 4:1 methanol-sulfuric acid solution. D. Corresponding histograms representing the stability results.
Table 1. Selectivity of the designed sensor for Trp detection in the presence of interfering species (0.1 M PBS, pH = 7).

Table 2. The results of the Trp assay and recovery tests in the real samples applying the designed sensing assay (n = 3).

研究结论
本研究成功开发了一种基于MWCNT-COOH/PDA-MIP的超灵敏电化学传感器,实现了对色氨酸的高选择性、宽线性范围及超低检测限的精准检测。该传感器在真实生物样本(血清、牛奶)中表现出优异的回收率与稳定性,为疾病诊断、食品质量监控及药物分析提供了可靠工具。未来可通过替换模板分子拓展至其他生物分子检测,具备规模化应用与便携式设备开发的潜力。
免责声明:原创仅代表原创编译,水平有限,仅供学术交流,如有侵权,请联系删除,文献解读如有疏漏之处,我们深表歉意。


公众号丨智能传感与脑机接口











![2025年中国力矩传感器行业发展现状、竞争格局及趋势研判:下游机器人技术快速发展,带动力矩传感器规模达9.5亿元[图]](https://xtechcon-static.oss-cn-chengdu.aliyuncs.com/xtimes/xtimes/images/2025-11-22/69210b9e140b8.jpeg)